In this post, we’ll walk you through a (very) brief history of NoSQL, then explain the main types of NoSQL databases with examples and use cases for each.
The tl;dr History of NoSQL
(It actually stands for “not only SQL”)
Coined in 1998 by Carlo Strozzi, the creator of the open-source relational database Strozzi NoSQL, the first use of the term “NoSQL” had nothing to do with the term as we use it today.
It took a good decade for the term to hit mainstream, thanks to a successful Twitter hashtag which described the then-database advancements at the time. Today, NoSQL databases account for 3% of the database market. And growing.
Non-relational or NoSQL databases were born out of the rigidity of traditional relational or SQL databases, which use tables, columns, and rows to establish relationships across data.
Developers welcomed NoSQL databases because they didn’t require an upfront schema design; they were able to go straight to development. And it’s this flexibility – this “ad-hoc” approach to organizing data – that has arguably been NoSQL’s greatest selling point, which continues to appeal to companies that need to store unstructured or rapidly changing data.
NoSQL Database Types
Some articles mention four main types, others six, but in this post we’ll go through the five main types of NoSQL databases, namely wide-column store, document store, key-value store, graph store, and multi-model.
Wide-Column Store
As the name suggests, wide-column stores use columns to store data. You can group related columns into column families. Individual rows then constitute a column family.
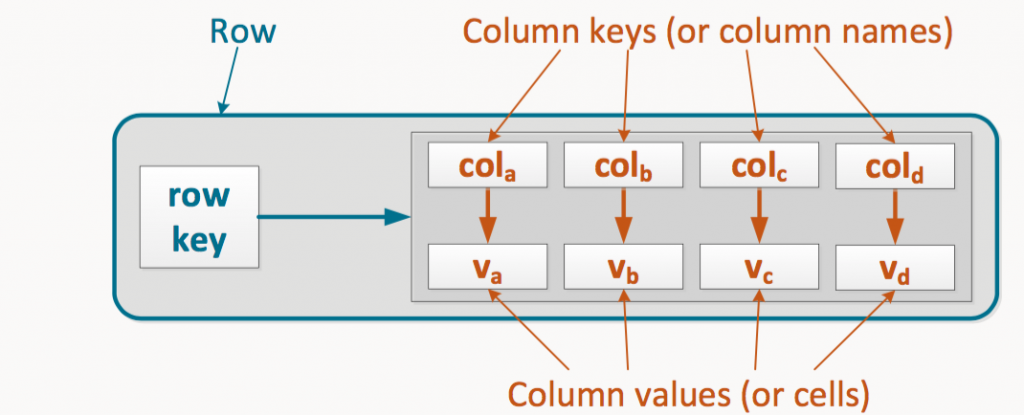
Sounds a bit confusing, doesn’t it? Visuals should help. Here’s what an individual row within a column family looks like in Cassandra:
(Source)
A typical column family contains a row key as the first column, which uniquely identifies that row within the column family. The following columns then contain a column key, which uniquely identifies that column within the row, so that you can query their corresponding column values.
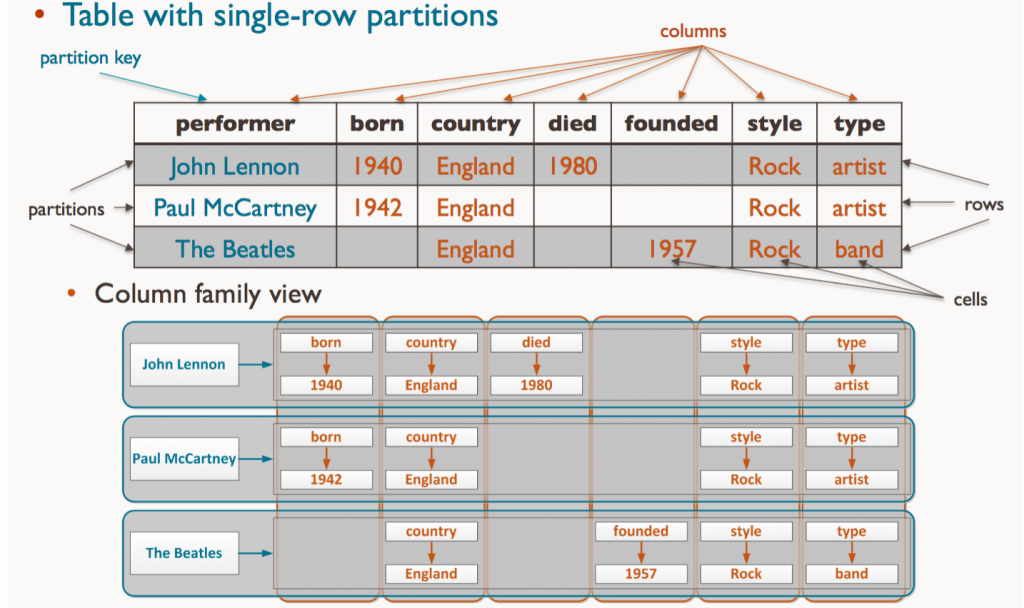
To better illustrate, here’s how data in a table would translate to a column family:
(Source)
Examples of Column Databases
Use Cases
Column stores offer very high performance and a highly scalable architecture. Because they’re fast to load and query, they’ve been popular among companies and organizations dealing with big data, IoT, and user recommendation and personalization engines.
- Spotify uses Cassandra to store user profile attributes and metadata about artists, songs, etc. for better personalization
- Facebook initially built its revamped Messages on top of HBase but is now also used for other Facebook services like the Nearby Friends feature and search indexing
- Outbrain uses Cassandra to serve over 190 billion personalized content recommendations each month
Document Store
Document store databases use JSON, XML, or BSON documents to store data. You can pretty much fill in a document with whatever data you want. Documents can have different structures, but you can index common fields for faster performance.
Here’s an example of a document in MongoDB:

(Source)
Examples of Document Databases
- MongoDB – Free, open-source (ranked by many as the top NoSQL database to learn and voted by Stack Overflow devs as the the most wanted database for the 4th consecutive year)
- Couchbase – Free, open-source
Use Cases
- SEGA uses MongoDB for handling 11 million in-game accounts
- Cisco moved its VSRM (video session and research manager) platform to Couchbase to achieve greater scalability
- Aer Lingus uses MongoDB with Studio 3T to handle ticketing and internal apps
- Built on MongoDB, The Weather Channel’s iOS and Android apps deliver weather alerts to 40 million users in real-time
Thinking of choosing MongoDB?
If you’re considering MongoDB, be productive from day one and download Studio 3T, the most powerful MongoDB GUI available.

Still learning the MongoDB query language knowledge? No problem. Build queries visually by dragging and dropping fields, or use SQL to query MongoDB.
Or if you’re already a pro, enjoy powerful features like query autocompletion, stage-by-stage aggregation editor building, instant code generation, and much more.
Key-Value Data Store
Key-value databases store data in unique key-value pairs, meaning each key is associated only with one value in a collection, like in a dictionary. This makes querying a key-value data store fast because of its simple model. There’s no query language needed. Data retrieval is a simple matter of using get, put, and delete commands.
Examples
Use cases
Key-value data stores are ideal for storing user profiles, blog comments, product recommendations, and session information.
- Twitter uses Redis to deliver your Twitter timeline
- Pinterest uses Redis to store lists of users, followers, unfollowers, boards, and more
- Coinbase uses Redis to enforce rate limits and guarantee correctness of Bitcoin transactions
- Quora uses Memcached to cache results from slower, persistent databases
Graph Store
Nodes and relationships are the bases of graph databases. A node represents an entity, like a user, category, or a piece of data. A relationship represents how two nodes are associated.
Graph databases use nodes that contain lists of relationship records. These records represent relationships with other nodes, which eliminates the (time-consuming) search-match operation found in relational databases.
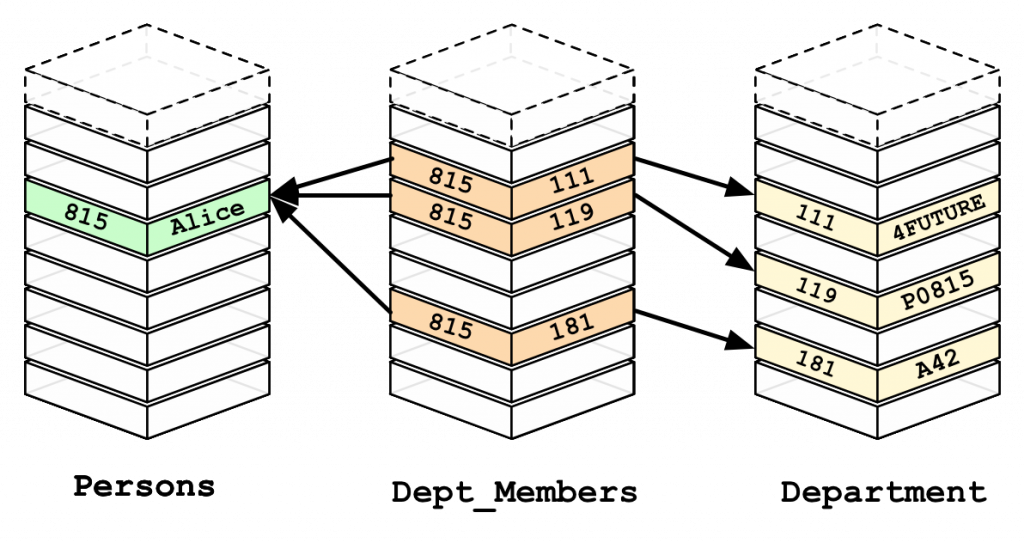
The image below shows how a relational database like MySQL works, which use memory-intensive and more complicated join operations to search entire tables to find a match:
(Source)
Compare that to a graph database, which already predetermines relationships based on connected nodes, making queries much faster and more economical.
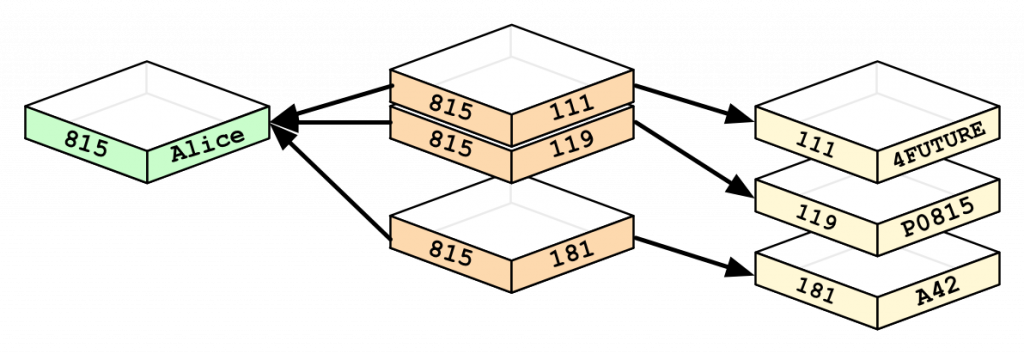
(Source)
Examples of Graph Databases
- Neo4j – Free, open-source
- JanusGraph – Free, open-source
Use Cases
Graph databases are great for establishing data relationships especially when dealing with large data sets. They offer blazing fast query performance that relational databases cannot compete with, especially as data grows much deeper.
- Walmart uses Neo4j to provide customers personalized, relevant product recommendations and promotions
- Medium uses Neo4j to build their social graph to enhance content personalization
- Cisco uses Neo4j to mine customer support cases to anticipate bugs
Multi-Model
It’s clear that the four previous NoSQL database types have their respective advantages, which is why the multi-model database has emerged as another popular option in recent years. As its name suggests, a multi-model database combines the capabilities of wide-column, graph, document, and key-value databases. More supported data models within one database means more versatility for you – the end user – in the way you store your data.
Examples of Multi-Model Databases
- Microsoft Azure Cosmos DB – Pricing starts at $0.25/GB, free Emulator available
- OrientDB – Free, open source
Use Cases
- RTE’s Investigations Unit uses OrientDB to establish data connections across various sources for investigative purposes
- Azure CosmosDB supports Citrix’s Identity Platform, which enables single-sign on for more than 400,000 organizations and 100 million individuals worldwide
- ASOS uses Azure Cosmos DB to deliver real-time product recommendations and instant order updates for 15.4 million customers
We hope this guide helps you get an idea of which NoSQL database type to choose for your app or project.
And don’t forget – if you’ve already identified MongoDB as the database for the job, get more done and download Studio 3T, available for Windows, macOS, and Linux.









