When you start with MongoDB, the find() command for querying data will probably be sufficient, but as soon as you start doing anything more advanced than data retrieval, you will need to know more about the MongoDB aggregation pipeline.
The MongoDB aggregation pipeline consists of stages. Each stage transforms the documents as they pass through the pipeline.
Here’s an example of a simple, typical MongoDB aggregation pipeline which uses four common aggregation stages:
$match()– filters those documents we need to work with, those that fit our needs$group()– does the aggregation job$sort()– sorts the resulting documents the way we require (ascending or descending)$project()– to return only those fields you need so as to avoid processing more data than is necessary
Common uses for aggregation include:
- Grouping data by a given expression
- Calculating results based on multiple fields and storing those results in a new field
- Filtering data to return a subset that matches the given criteria
- Sorting data
There are a myriad of MongoDB tools available, offering features like schema visualization, code auto-completion, data import/export, and so on – but only a few offer a dedicated MongoDB aggregation feature.
To help you make filtering, transforming, sorting, computing, and aggregating your data easier, here are three MongoDB aggregation tools you can use.
MongoDB Aggregation Editor in Studio 3T
Studio 3T introduced the Aggregation Editor in 2015, becoming the first GUI (other than MongoDB Compass) to enable its users to build accurate aggregation queries.
It also made debugging easier by defining stage operators and checking inputs and outputs at each stage.
Its editor has since then been made better by adding support for additional aggregation stages, giving an option to copy and paste aggregation stages, the ability to export results to another collection, CSV, JSON, SQL, or mongodump, and disable pipeline stages temporarily, and many more.
“Studio 3T is the tops for me. In only 30 minutes, I can gain one whole day of work when building aggregation queries.”
– Pierre Yves Folens, DevOps Engineer at Orange
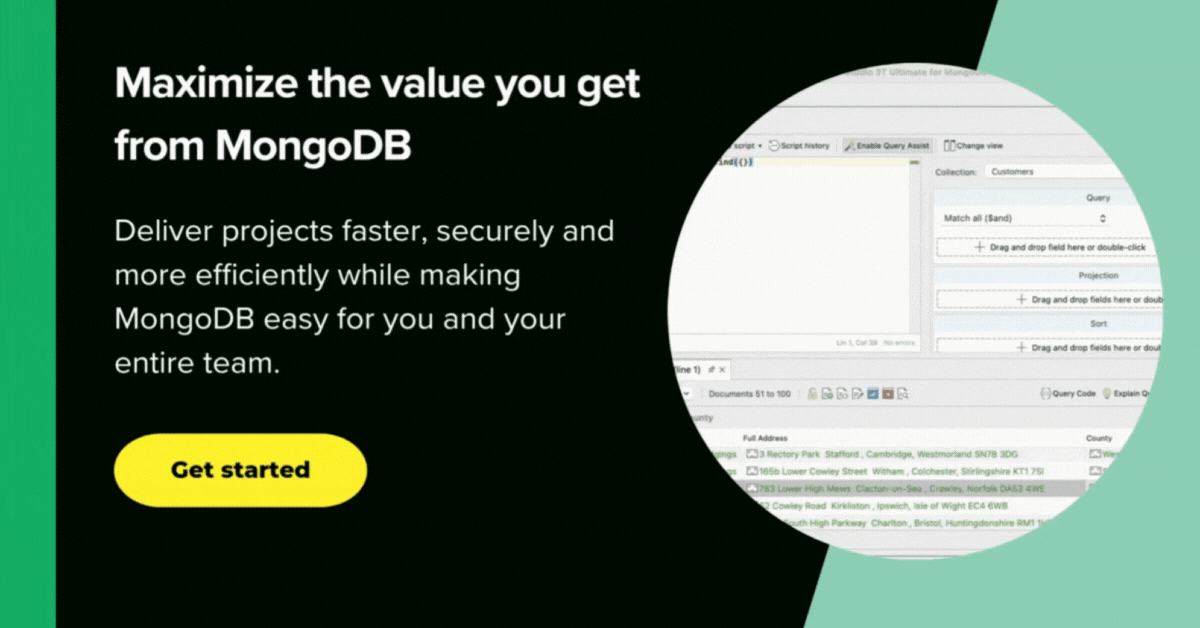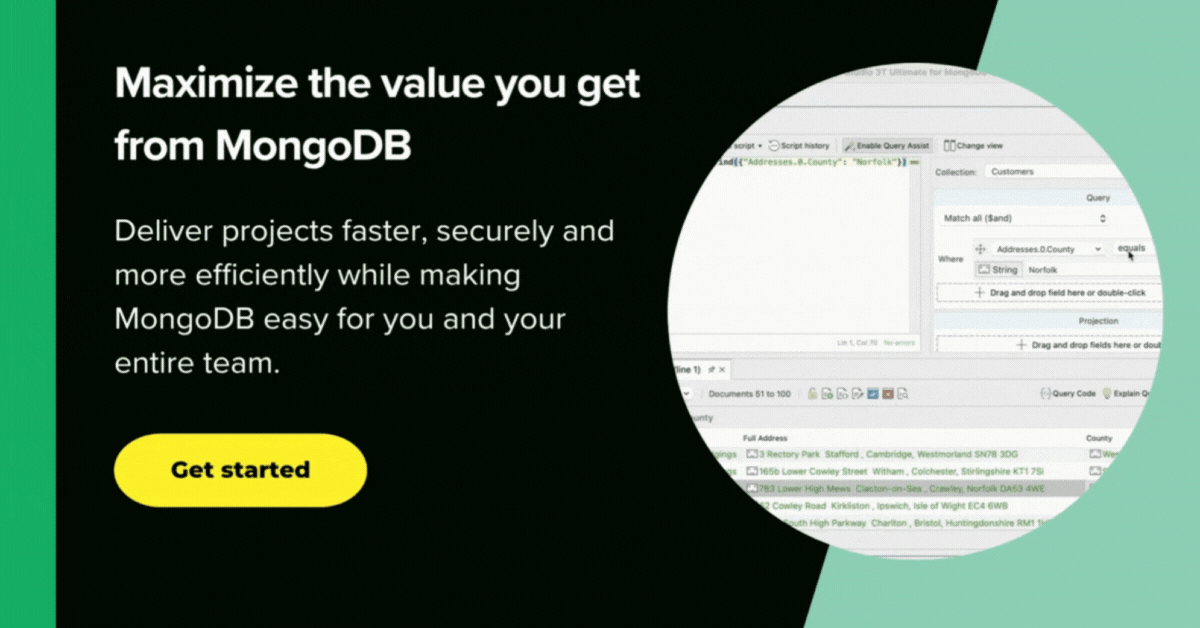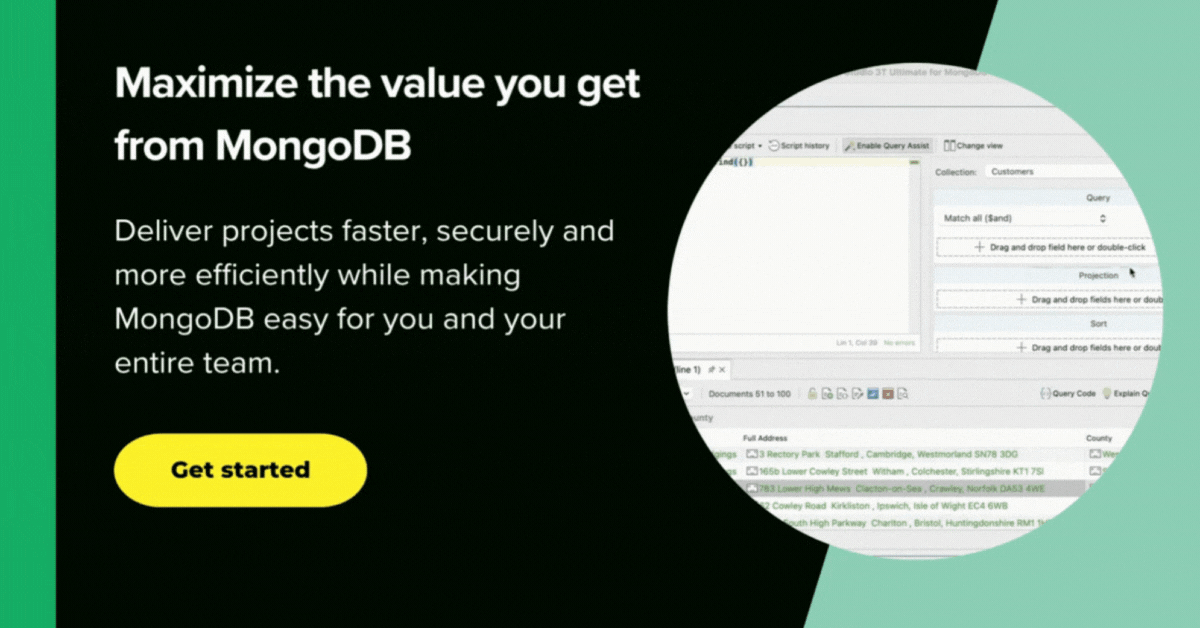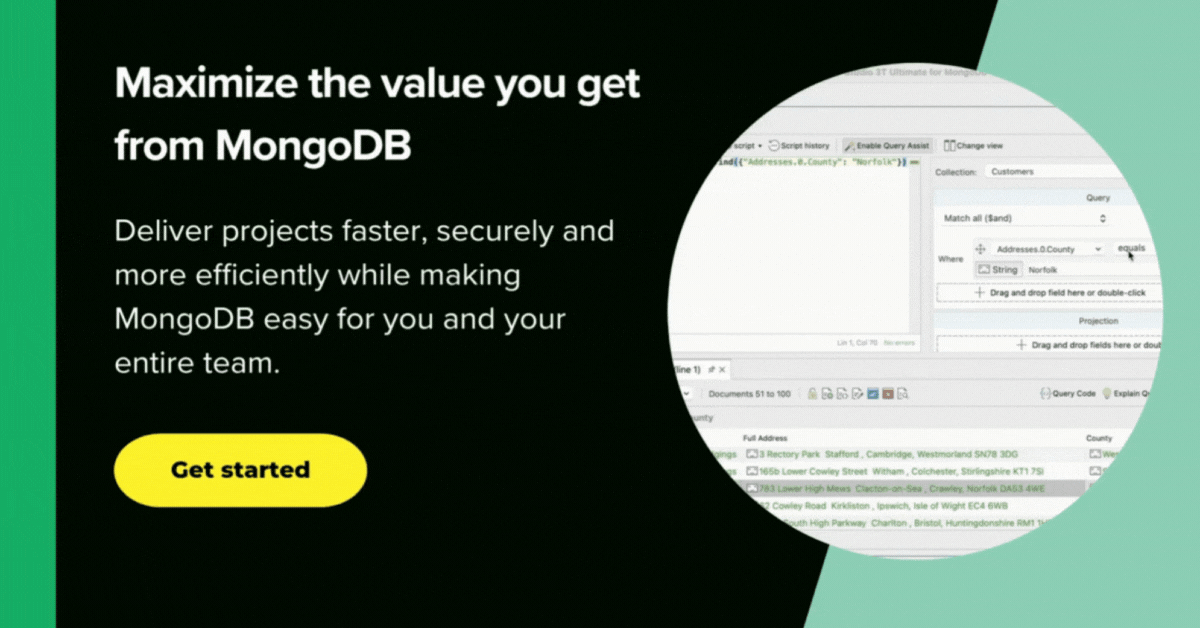
You can break down a complex query into easier stages. In each of these stages, you complete a different operation on the data. This approach allows you to check whether your query is functioning properly at every stage by examining both its input and output.
There is no limit to the number of stages used in the query, or how you combine them.
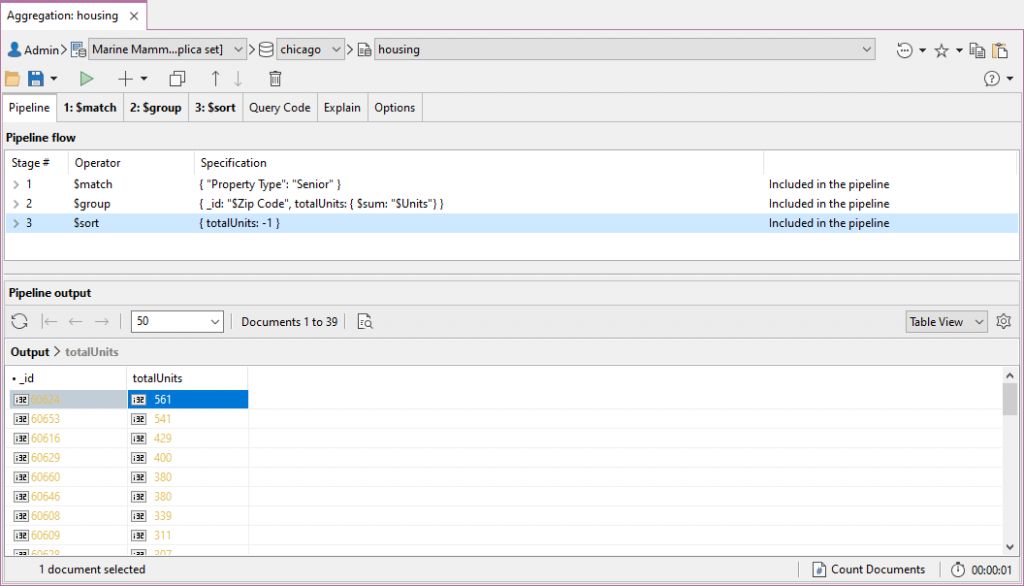
Source: Aggregation Editor in Studio 3T
You can see all your aggregation stages at a glance and add, edit, duplicate, and move as needed in the Pipeline tab. You can also view each stage in your pipeline individually, where you can edit and analyze your input and output stages individually.
Studio 3T’s aggregation editor also lets you translate your aggregation query to JavaScript (Node.js), Java (2.x, and 3.x driver API), Python, C#, PHP, Ruby, and the mongo shell language.
Aggregation Pipeline Builder in MongoDB Compass
MongoDB Compass is the GUI tool for MongoDB to visualize and query data, and they added a MongoDB aggregation pipeline builder to it in 2018. The aggregation pipeline builder provides the ability to create aggregations in a simple and real-time manner.
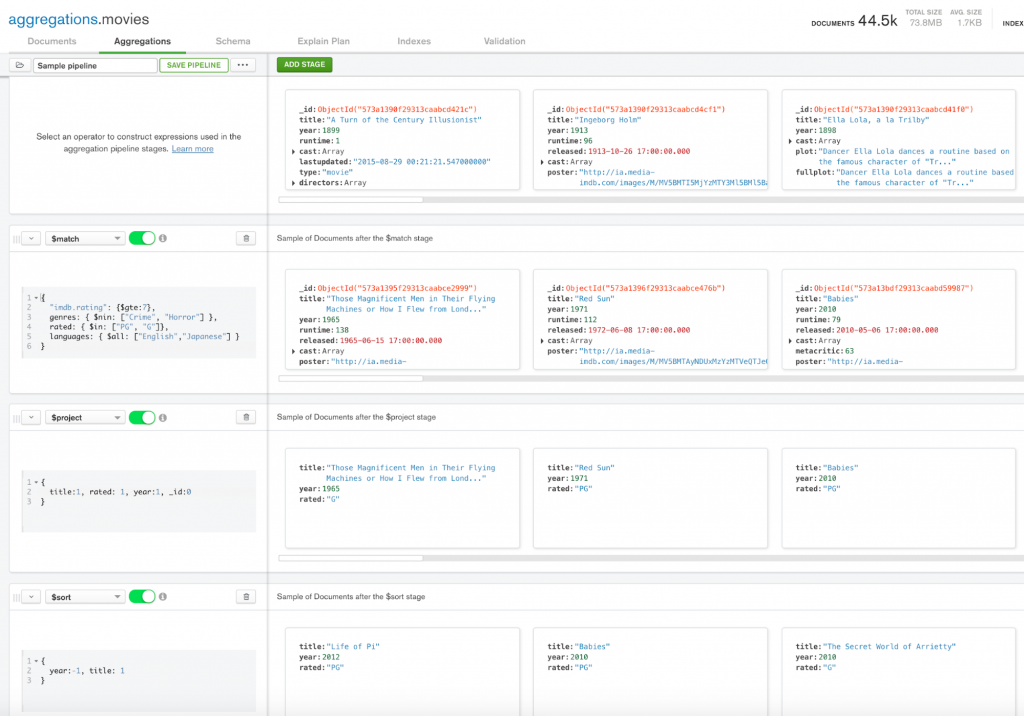
Source: MongoDB
As you select different aggregation stages to execute from drop-down boxes on the left side of the screen, the results of those actions are shown on the right side of the screen. You can add as many stages as you want, and save or clone pipelines as needed.
When you are done building a pipeline, you can copy it to the clipboard. The resulting JSON code can then be executed against the MongoDB database using the shell environment.
You can use the Aggregation Pipeline Builder to export your finished pipeline to only some of the few supported languages though: Java, Node, C#, and Python 3, unlike the wider range of options available with other tools.
The mongo Shell
The most basic way to access MongoDB is through the mongo Shell, an interactive JavaScript interface to MongoDB. You can use it to query, update data, and complete admin tasks.
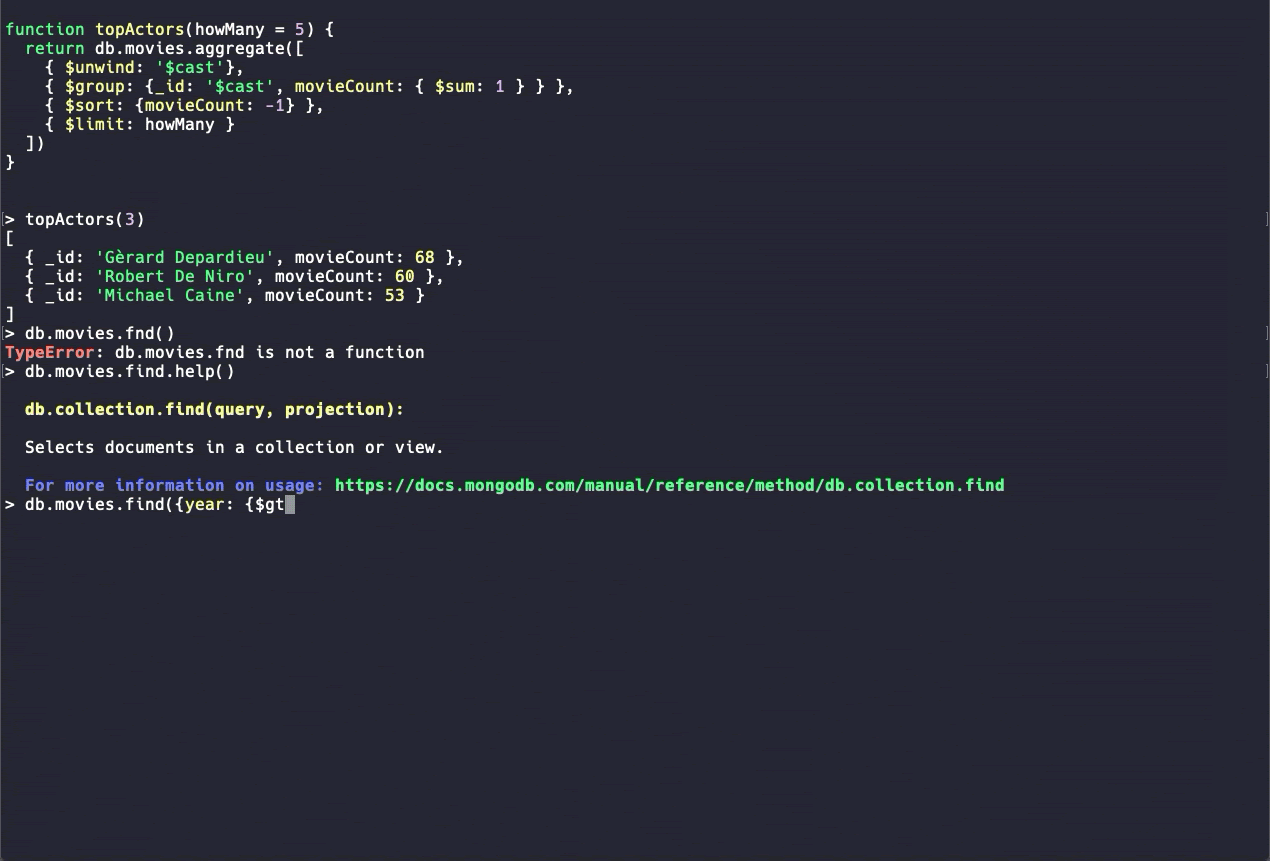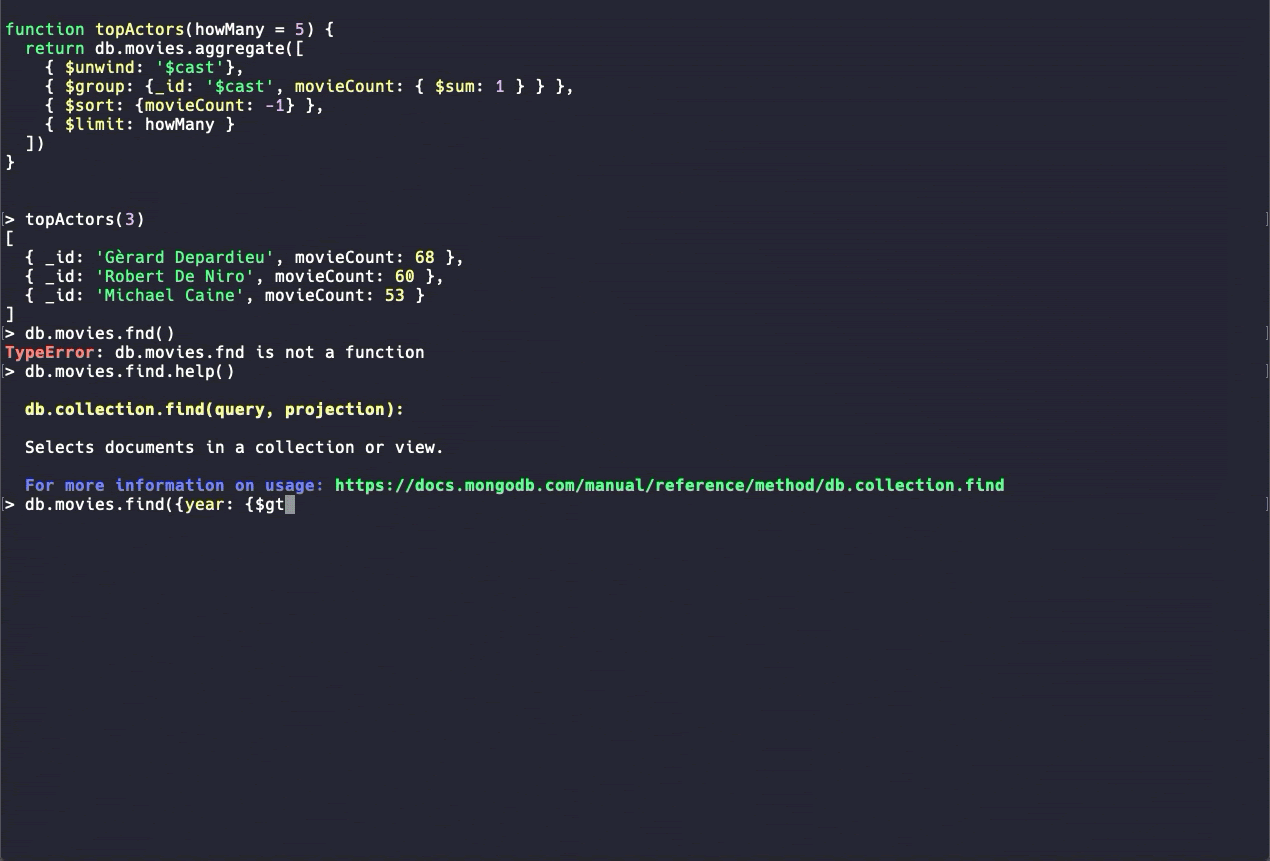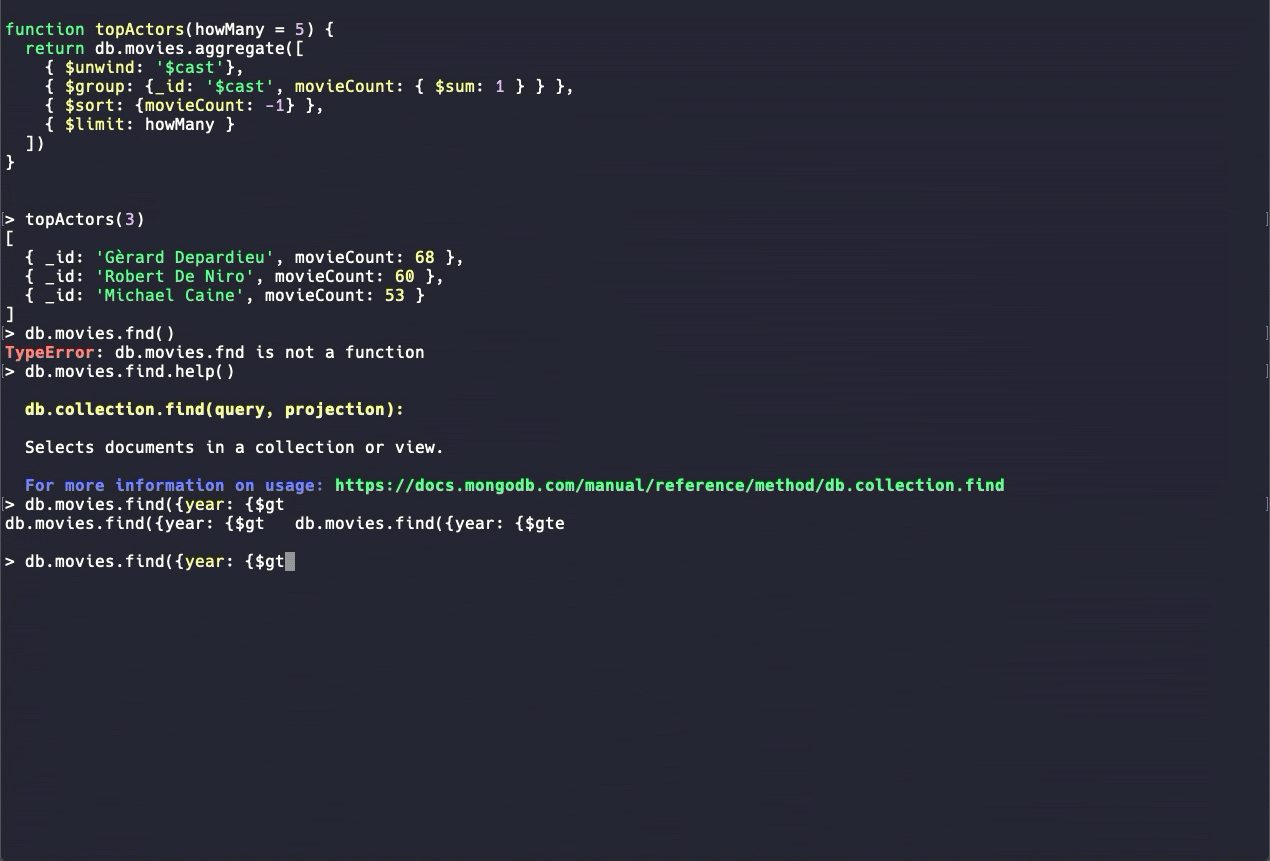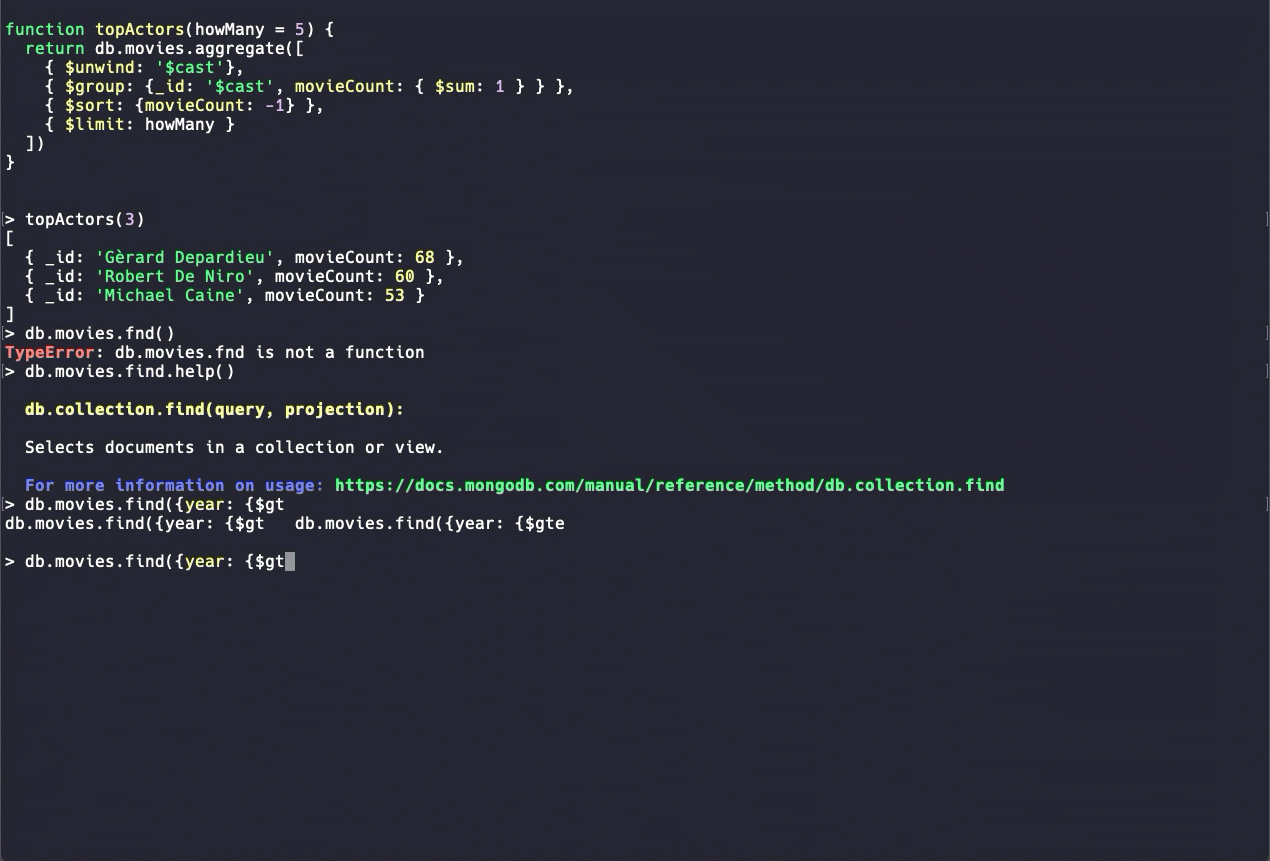
Source: MongoDB
It’s included in the MongoDB server installation, so you’re all set as long as you’re comfortable with shell commands.
While you can certainly use the mongo Shell to build your aggregation queries, traversing objects and writing long queries in the command line can get annoying fast, so using the shell is usually best for quick peeks or admin tasks.
To create an aggregation pipeline in the mongo Shell, you can use the following syntax:
db..aggregate([
{
<$stage1>
},
{
<$stage2>
}
...
])
MongoDB provides the db.collection.aggregate() method in the mongo Shell and the aggregate command to run the aggregation pipeline. The mongo Shell outputs the results directly to the terminal.
The MongoDB aggregation pipeline is an incredibly powerful framework for analyzing and abstracting data. While writing aggregation queries can get tricky, there are tools to help make building and debugging your pipeline in a matter of minutes instead of days.